Belgium

Basic Data
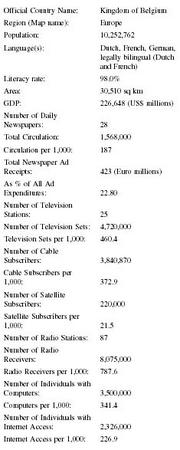
| Official Country Name: | Kingdom of Belgium |
| Region (Map name): | Europe |
| Population: | 10,252,762 |
| Language(s): | Dutch, French, German, legally bilingual (Dutch and French) |
| Literacy rate: | 98.0% |
| Area: | 30,510 sq km |
| GDP: | 226,648 (US$ millions) |
| Number of Daily Newspapers: | 28 |
| Total Circulation: | 1,568,000 |
| Circulation per 1,000: | 187 |
| Total Newspaper Ad Receipts: | 423 (Euro millions) |
| As % of All Ad Expenditures: | 22.80 |
| Number of Television Stations: | 25 |
| Number of Television Sets: | 4,720,000 |
| Television Sets per 1,000: | 460.4 |
| Number of Cable Subscribers: | 3,840,870 |
| Cable Subscribers per 1,000: | 372.9 |
| Number of Satellite Subscribers: | 220,000 |
| Satellite Subscribers per 1,000: | 21.5 |
| Number of Radio Stations: | 87 |
| Number of Radio Receivers: | 8,075,000 |
| Radio Receivers per 1,000: | 787.6 |
| Number of Individuals with Computers: | 3,500,000 |
| Computers per 1,000: | 341.4 |
| Number of Individuals with Internet Access: | 2,326,000 |
| Internet Access per 1,000: | 226.9 |
Background & General Characteristics
Belgium's media landscape—and position in European leadership—is not described by its small land mass of over 30 thousand square kilometers. Nor do its dense population of 336 people per square kilometers and its economic viability explain its lively and diverse press. To understand its press, one must understand Belgium's historical resilience as a nation often subjected to invasion and occupation, and its status as a multilingual but linguistically segmented country.
Before housing the leadership of the European Union (EU), Belgium, which derives its name from the Belgae Celtic tribe, was a province of Rome. When Attila the Hun invaded what is now Germany, Germanic tribes pushed into what is now Belgium. Next the Franks took control of Belgium. Oversight of Belgium next passed to the Spanish (1519-1713) and then to the Austrians (1713-1794). After the French Revolution, Belgium was annexed by Napoleon. It was made a part of the Netherlands in 1815. In 1830, after a revolution, Belgium declared its independence and established a constitutional monarchy. The result of a coalition of the intellectual and financial elite, Catholic leadership, and the nobility, the new nation's Constitution "may be considered a balanced compromise of the sometimes divergent interests of these social groups" (Lamberts 314). While Belgium was occupied by the Germans during both world wars, it survived and thrived when it was liberated in 1944 by Allied forces. The early and late occupations created a nation indebted to German, French, and Dutch influences. The nation has incorporated these languages and cultural elements into different parts of its geographic and cultural landscape. Belgium's characteristic compromise may be what makes it a desirable location for EU leadership despite its lack of central proximity.
The sustained balance of three diverse regions and language communities largely explains the development and fragmented organization of the press that serves its 10 million people. The Flemish, French, and German cultural communities were granted official autonomy with a 1970 revision of the Constitution that also established three separate economic regions: Flanders, Wallonia, and Brussels. Today, after a 1993 Constitutional revision, Belgium is a federal state with three distinct regions, each with its own prime minister, council of ministers, and regional council. In the north, Flanders largely sustains a Dutch speaking community, previously referred to as Flemish, represented by a Flemish community council. In the south, Wallonia is the home of a largely French speaking community who are represented by a French community council; eastern Wallonia, however, houses a significant German speaking population who are represented by a German community council. Brussels, the capital, is a multilingual community; the French speaking people are represented by a French community council who also represent Wallonia, while the Dutch speaking members of Brussels are represented with the Dutch speakers of Flanders in a Flemish community council. While there are numerous political parties on the Belgian scene, the three major political groups—Socialists, Liberal, and Christian Social—have French-and Dutch-language parties, respectively, and are largely organized along linguistic lines. The Flemings make up 60 percent of the population (Flanders 55 percent), and the Walloons make up about 30 percent (Wallonia 35 percent). About 1 percent of the remaining Belgians are German speakers who live in Eastern Wallonia on the German border.
Literacy in Belgium is reportedly 98 percent or better. Preschool education, which begins at two and one-half years of age, is very popular and successful; more than 90 percent of Belgian youngsters attend. Education is compulsory from 6 to 18 years of age. During comprehensive education, all students specialize in technical, vocational, or college preparatory curriculum. Its oldest university, established in 1425, is the Catholic University of Louvain. In 1834 the Free Masons established the Free University of Brussels. Because of the legally bilingual nature of Belgium, both universities operate separate French and Dutch speaking campuses. A state university system was also established in Ghent and Liege in the early 1800s; other schools have followed in the 1900s. The government subsidizes 95 percent of student expenses. All these factors contribute to a highly educated and skilled workforce.
While the Belgian people are highly literate, most do not subscribe to a daily newspaper. Increasing pressure to maintain or enlarge circulation has encouraged many dailies to adopt a "tabloid" style to their presentation. The World Association of Newspapers (WAN) reports that many newspapers have also decreased the number of pages in their daily publications, making the texts more compact. In 1995 "the overall circulation of the Belgian press amounted to 1,543,623, the Flemish press taking 993,229 or 64.3 per cent of sales, and the French-language press 550.394 or 35.6 per cent of sales" (de Bens 2). Only about 36 percent of Belgians were reported to subscribe to a newspaper in 1995 (2). While circulation figures have declined in the latter part of the 1990s, tabloid strategies have reportedly been adopted by many dailies to enhance their market share. From 1996 to 2000 circulation declined 3.3 percent overall in Belgium. While WAN further reports that Belgian daily circulation increased slightly, 0.2 percent in 2000, overall newspaper sales in the European Union have fallen 2.5 percent from 1996. A May 2002 conference hosted by WAN examined strategies to revamp Web sites and enlarge circulation in
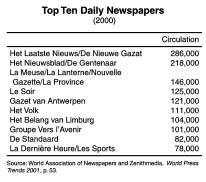
Of the 41 newspapers published in Belgium, most are dailies. Belgians additionally have ready access to both EU and non-European publications. Circulation figures gathered within the 135th Edition of the Gale Directory of Publication and Broadcast Media (2001) indicate that 14 newspapers have a circulation of 100,000 to 500,000. About six publications have circulation figures in the range from 50,000 to 100,000, an additional six have circulation figures from 25,000 to 50,000, and five have circulation figures of 10,000 to 25,000. The rest have circulation rates of less than 10,000 copies. Of the 11 largest daily Belgian newspapers by circulation, 8 serve the Dutch speaking community; 3 are published in French. Note that these figures may vary from source to source. Of the Dutch publications, De Standaard/Het Nieuwsblad/De Dentenaar, established in 1914, has a circulation of 372,410; De Gentenaar, established in 1879, has a circulation of 372,410; Het Laatste Nieuws, established in 1888, has a circulation of 308,808; De Nieuwe Gazet, established in 1897, has a circulation of 306,240; Gazet Van Mechelen, established in 1896, has a circulation of 177,898; De Nieuwe Gids, established in 1955, has a circulation of 171,350; Gazet Van Antwerpen, established in 1891, has a circulation of 148,095; and Het Volk, established in 1891, has a circulation of 143,330. The French publications with large circulation figures are: Le Soir, established in 1887, which circulates 178,569 copies; L'Avenir Du Luxembourg, established in 1897, which circulates 139,960 copies; and Vers L'Avenir, established in 1918, which circulates 139,960 copies. The only German daily, Grenz Echo, a Catholic publication founded in 1927, has a circulation of 12,040.
The many newspapers vary not only in their language of publication but also in their coverage and target audience. De Standaard, one of two dailies that share the largest circulation status, is decidedly the most strident Flemish nationalist newspaper. Het Laatste Nieuws, which shares De Standaard's circulation breadth, De Morgen, La Derniere Heure are less nationalistic, characterized as progressive-liberal newspapers, with a "relatively lowbrow populist tone" (Elliott 187). Le Soir is a respected French daily; La Libre Belgique sports a "perceived upper-class readership and a firmly 'keep-Belgium-united' stance" (187). Business coverage comes in the form of L'Echo, French, and De Financieel-Ekonomische Tidj, Dutch. English favorites such as The Wall Street Journal, The Financial Times, The Times and the Herald Tribune are all reprinted for a Belgian audience.
Economic Framework
Initially most newspapers were offshoots or instruments of a political party, union, or pillar, such as the Catholic Church, the liberals, and the socialists (Witte 290; Lamberts 328). While the Catholic Church and the liberals still hold a strong representation in newspapers, papers today are increasingly held by large conglomerates, thus making the papers a little more ideologically independent. Financial constraints have virtually eliminated small party representation in the press, and as such Socialist Party coverage was diminished entirely (the Volksgazet and Le Peuple ) or was redirected toward a more general public ( De Morgen ), thereby obscuring party affiliation (Lamberts 291). Starting in the 1960s, newspapers have been increasingly absorbed by these large conglomerates, thereby decreasing competition. Of the cities with circulation statistics available, 29 appear to have competition, whereas 9 (roughly 25 percent) do not. Only about 10 newspapers are truly autonomous; the remaining publications vary only slightly in coverage and format from the market leaders (de Bens 1).
In Flanders three conglomerates dominate the newspaper business. Vlaamse Uitgeversmaatschappij (VUM) publishes De Standaard, Het Nieuwsblad, De Gentenaar, and Het Volk. De Persgroep owns Het Laatste Nieuws, De Nieuwe Gazet, and De Morgen. Regionale Uitgeversmaatschappij (de RUG), an alliance between N.V. De Vlijt and N.V. Concentra, publish Gazet van Antwerpen and Het Belang van Limburg (Witte 290; de Bens 1).
Until 1998 the Francophone press was dominated by three groups: 1) N. V. Rossel, who owns Le Soir, La Meuse, La Lanterne, La Nouvelle Gazette, La Province;2) IPM who owns La Libre Belgique and La Derniere Heure; and 3) Mediabel, who publishes Vers l'Avenir, Le Jour/Le Belgique, La Courrier de l'Escaut, l'Avenir de Luxembourg, and Le Rappel (de Bens 1). The Franco-phone press is nearing duopoly status because Vers l'Avenir acquired 51 percent of IPM in the late 1990s (de Bens 2). As a result, readers of one publication have banded together in a readers' association to demand diversity of the press and editorial staff independence (1998 World Press Freedom Review). Finally, while the German speaking region has Grenz Echo, published by an independent publishing house, Rossel now owns 51 percent of Grenz Echo shares.
In 1995 Belgian press circulation was 1,543,623; the Flemish press accounted for 993,229 or 64.3 percent of sales, while the French-language press accounted for 550.394 or 35.6 per cent of sales (de Bens 2). Only about 36 percent of Belgians are reported to subscribe to a newspaper (2). As circulation figures have declined in the latter part of the 1990s, strategies have reportedly been adopted by many dailies to enhance their market tabloid share (de Bens; Elliott). VUM and Rossel have adapted well and are market leaders in sales and advertising revenue (de Bens 2).
While newspapers are attempting to make an economic comeback, 1999 layoffs in smaller regional papers that regrouped in Sud-Presse and layoffs in the national wire service sorely tested efforts to offer diverse press coverage. It appears that readership in Brussels and the Dutch speaking regions of Belgium is increasing, as it is decreasing in the Francophone region (1999 World Press Freedom Review). The print media is largely free of subsidies that it was granted in 1975; subsidies were found to have little effect on market trends and/or to be too small to make a difference (de Bens 4). In 1999 Flanders eliminated direct subsidies because all of its newspapers had been bought by larger media groups. While direct subsidies are decreasing, indirect assistance remains. The print media continues to operate value added tax (VAT) free today, thereby assisting the struggling newspaper and magazine market.
Press Laws
Title II of the Constitution, "Belgians and Their Rights," includes three articles that have bearing on the press. Article 25 specifically grants Belgians the right to a free press: "censorship can never be established; security from authors, publishers, or printers cannot be demanded." It further states that when the author is a known resident of Belgium, neither the publisher, nor the printer, nor the distributor can be prosecuted" (Adopted 1970, as revised 1993). In addition to establishing a free press, Article 25 also protects Belgian journalists and publishers from prosecution—or, so it would seem. Contemporary cases that challenge this protection include the 1990s Dutroux pedophilia case and the 2002 fining of two De Morgen journalists.
Article 19 [Freedom of Expression] grants Belgians, "freedom of worship, public practice of the latter, as well as freedom to demonstrate one's opinions on all matters." The Constitution also includes a Freedom of Information clause; according to Article 32, "Everyone has the right to consult any administrative document and to have a copy made, except in the cases and conditions stipulated by the laws, decrees, or ruling referred in Article 134." In addition to its own constitutional provisions, as a member of the EU, Belgium is party to a Green Paper that seeks to broaden access to public documents and extend freedom of information across Europe.
The Belgian media is not tightly regulated by extra-constitutional legal provisions; most of the laws and statutes guiding press actions are characterized by insiders as ambiguous. Belgium leadership is therefore often criticized by human rights groups and liberals for pursuing a largely laissez-faire media policy (de Bens 4). To fill this regulation void, the Belgian Association of Newspaper Publishers, the General Association of Professional Journalists of Belgium, and the National Federation of the Information Newsletters came together in the Belgium Press Council and drafted the Belgium Code of Journalistic Principles in 1982. This Code articulates the importance of: 1) a free press; 2) unbiased collecting and reporting of facts; 3) separation of facts reported and commentary on the facts; 4) respect for a diversity of opinions and publishing of different points of view; 5) respect for human dignity and the right to a private life make it necessary to avoid physical and/or moral intrusion; 6) restraint from glorifying violence; 7) commitment to correct previously reported false information; 8) protection of source confidentially ; 9) thwarting efforts to prevent freedom of press in the name of secrecy; 10) editorial judgment when freedom of expression appears to conflict with fundamental human rights; 11) resisting outside pressure on newspapers and journalists; and 12) presenting advertisements in such a way as not to be confused with facts (International Journalists' Network). The Code continues to be the most important regulator of press conduct in Belgium despite efforts to draft laws and statutes that guide the behavior and legal treatment of journalists.
As of result of 1990s scandals, the Minister of Justice convened a hearing for interested parties such as judges, lawyers, politicians, journalists, and academic experts, where issues such as the protection of sources for journalists, treatment of press trials, and the need for an Order of Journalists were discussed. Conflict, particularly about ethical issues, made the implementation of laws too difficult; it was decided that the journalistic codes should continue to handle ethical problems. The Belgian Press continues to be self-regulated by the Federation of Editors—a body to which all newspaper editors belong.
Starting in the late 1990s, there was much discussion of bringing press violations such as advertising, tract distribution, and racism to magistrate courts, whereas "ordinary" violations would still be evaluated by a jury per the Belgian Constitution (1998 World Press Freedom Review). Amendments to the "right of reply" also have been examined but not enacted.
While a 1998 law had mandated speech to the press from the highest public prosecutor, journalists complained that contact was difficult to establish. Minister of Justice Tony Van Parys, therefore, ordered that prosecutors needed to designate spokespeople who could provide journalists with investigation updates in 1999 (World Press Freedom Review). Such a move was welcomed by journalists and press freedom groups.
Prior to 1980 the Belgian press was subject to the following laws: 1979 Press Law, 1987 Belgian Media Law, 1987 Flemish Speaking Law for Commercial Television, and the 1980 Royal Decree on Execution of the 1979 Press Law.
Censorship
Oversight of the press comes primarily in the form of a Deontological Council of the Belgian Association of Professional Journalists and its Code of Ethics. While Belgium's Constitution encourages an independent media, journalists are increasingly being targeted for lawsuits and/or to divulge confidential sources. Since 1999 journalists and the papers that employ them have increased their insurance policies to cover penalties imposed by Belgian courts (World Press Freedom Review). While the trend is for courts to fine journalists, this trend is often offset in appeal. Cases continue to be brought before Belgian courts, however, and many press freedom groups lament the trend.
In June 2002 Douglas de Conick and Marc Vendemeir, journalists for De Morgen, were fined 25 euros (approximately $23 per day) for failing to reveal their sources for a May 11, 2002, story in which they reported that the Belgian State Railway had overshot its budget for a high-speed train. The case will likely join a similar 1995 case on the docket of the European Court of Human Rights, a Strasbourg court that has often affirmed the right of journalists to keep their sources confidential.
On August 9, 2000, a Belgian court granted an emergency injunction to stop L'Investugatuer editor Jean Nicolas from publishing a list of convicted or suspected pedophiles. The court further ordered that if Nicolas failed to comply, circulation of the list would lead to a fine of about $22,000 per copy (2000 World Press Freedom Review). The court found that publishing the list would violate the rights of the accused. Journalists and Belgian citizens, however, saw this action as another example of court indifference to victims and potential victims.
On November 16, 1999, two Le Soir Illustr journalists were fined 55,000 euros for implying that a police officer had failed to make a proper inquiry into allegations of sex abuse by a minor. Likewise, fines were levied on Michel Bouffioux and Marie-Jeanne Van Heeswyck, Télé Moustique reporters, who labeled the same police officer a "manipulator" in their story (World Press Freedom Review). Reviewers argue that the lower courts are increasingly siding with public officials and law enforcement officers against the press.
In 1997 the police searched the office of Hans Van Scharen, a De Morgen journalist, and confiscated items related to his coverage of a "hormone mafia" case; he was accused of improperly possessing judicial documents (1997 World Press Freedom Review).
The most controversial cases, however, concern the 1996 Marc Dutroux case and a 1997 child custody case. Dutroux, a pedophile, raped and killed young Belgian girls. The press was very active in the investigation, while the government was seen to have foiled the case. The complete transcript of the case was made available to a Web site by a journalist; the Web site was later ordered shutdown. In the custody case, the justice system and judiciary were criticized for potentially favoring a notary who was accused of molesting his two sons. In both cases, the justice system was seen at odds with efforts of the press to secure justice. The European Court of Human Rights ruled that accusations made by the journalists appeared to be justified and awarded them legal costs of 851,697 Belgian francs (about US$24,500) (1997 World Press Freedom Review).
Therefore, while censorship is officially absent, Belgian courts' rulings against journalists in libel and source confidentiality cases, particularly where government or judicial figures are criticized, appear to be growing as of the late 1990s and early twenty-first century. Human rights advocacy groups and press freedom groups continue to watch the situation closely.
State-Press Relations
As the press law and censorships sections suggest, Belgium's print press is not subject to strong state control. Its audiovisual media, however, is primarily state run, but commercial and foreign expansion efforts have met a favorable climate. Telecommunications are over-seen by the Minister of Telecommunications, while the print news media is self-regulated.
All forms of the press can and do criticize the government. Until the mid-1990s, journalists faced few attempts to interfere with their reporting. Recent court cases levied by state officials may indicate a change in practice. A 1996 case particularly concerns international journalists and human rights groups. A licensed Kurdish station, MED-TV, was forced to close when the Belgian police raided its offices and confiscated its archives. The International Centre against Censorship argued that Belgium was bound by Article 19 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which among other things guarantees freedom of expression and the right to "seek, receive, and impart information."
The Belgian government has also done little to limit the creation of media conglomerates. Broadcast monopolies were legally legitimate until the late 1980s. On the more positive side, increased access to prosecutorial spokespeople has liberated the flow of information from the state to the citizen on important government and criminal matters.
Attitude toward Foreign Media
As the home of EU leadership, Belgium is frequented by and home to many international journalists. If there is a complaint about coverage in Belgium, it is that regional and national coverage of Belgium itself is often diminished in favor of covering EU issues.
According to non-Belgian journalists, it is very expensive to have a full-time correspondent in Brussels because it is at the periphery of Europe. While large agencies and organizations like Reuters and the BBC have people based in Belgium, some smaller countries and networks contract with a freelance journalist who supplies coverage to more than one agency. Belgium's specific coverage in other European countries is often limited because the correspondents largely address their coverage to EU issues.
News Agencies
Belgium has its own press agency, Belga Press Agency, which covers both daily national and international news. It was originally offered as the Belgium Telegraphic Press Agency ( Agence Belga ) in 1920. According to its home page timeline, the agency distributed its first press release on January 1, 1921, to 45 newspapers, 16 banks, the government, and 9 commercial companies. In 1925 Belga created its home desk; its editorial structure was split into a French-and Dutch-speaking desk in 1970. Using the Hermes system, Belga computerized its editorials and became the country's first electronic press company in 1981. This was followed in 1984 with real-time dispatches to the government's Bistel information network. A client-specific system was developed in 1986 to provide selective information to interested markets by fax or e-mail. Most recently in 2000 Belga entered a joint venture with news aktuell International, a subsidiary of the German Press Agency, to distribute specialized press releases. Today Belga dispatches information on politics, cultural issues, finance, sports, and public personalities in the public venue to the traditional media—newspapers, radio, and television. It also offers a subscription service for business and government clients. Belga's press releases are distributed to an international market, too, through contracts with the world's largest foreign press agencies. Belga prides itself for autonomy, accuracy, and timeliness
Foreign press agencies offer coverage in Belgium as well. Reuters Belgium is a regional office of Reuters International that supplies news information on business and finance. The BBC offers extensive coverage of Belgium.
Broadcast Media
Like the print media, television and radio are divided primarily along linguistic lines. As a result, many Belgians know their regional news and programs yet face limited access to information and stations of other Belgian regions in favor of programming from the rest of Europe and the United States (Elliott 184). It is quite likely that someone in Wallonia has more access to English and international programs than those from the Dutch regions of Belgium itself.
A number of private radio stations were aired after 1923, including Radio Belgique, which was supported by both the royals and the Belgian business world (Lamberts 359). The National Institute for Radio (NIR), a public radio network, was funded by the Belgian Parliament in 1930. It was modeled on the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC). Unlike the BBC, the NIR, however, was required to allocate air time for party-affiliated organizations, thereby limiting its objectivity and political investigative scope (Lamberts 359). The three main parties demanded broadcasting time; staffing was also influenced by the pillars who sought and gained an employment policy of proportional representation (Witte 291). Thus, the Belgian network, public by statute, was dominated by the country's religious and ideological pillars (Lamberts 359). This public monopoly effectively controlled the radio waves until a 1987 law that allowed for private broadcasting.
Public service programming is supported by an annual licensing fee on automobile radios. Home radios are not subject to licensing (Elliott 185). A ban on radio advertising was revoked in 1985, thus clearing the way for more commercial stations. While the political parties ensured that change was slow to take hold, the public service radio broadcaster currently struggles to survive amid competition from Internet news programming and commercially supported programming in the twenty-first century.
The main radio stations today continue to be state run. RTBF1 and VRT offer mixed programming. Radio 1 is one of the five public radio networks offered by the VRT. Radio Vlaaderen International (RVI) offers programming like "Flanders Today" for the Flemish speaking community as well. Radio 1's news and current affairs programs explore social issues and controversies, economic indicators, and cultural events in depth. Radio 2 is Flanders' largest radio network. It provides its listeners with local news and popular music. Radio 2 offers regional program coverage in the five Flemish provinces. Radio 3 is a high-brow station, targeted to the more liberal, intellectual listener. Radio 21 plays current releases and news to the Francophone population, whereas StuBru offers such tunes and coverage to the Dutch speaking community. The BBC World Service is offered in both English and German. There are over 79 FM, 7 AM, and 1 short-wave stations as of 1998. There are over 8.075 million radios in the country; access to radio coverage and alternative programming, however, has broadened substantially with Internet radio coverage.
Belgian television began in 1953 and has become an important information and leisure tool. Like Belgian radio, television was initially dominated by a public monopoly. By the 1980s, however, these monopolies were challenged by commercial stations that were allowed to broadcast their own programs. Since the introduction of audiovisual media, the print media has lost subscriptions, leading to the many mergers. For a time before the mergers, starting in 1975, subsidies were used to sustain the print media (Lamberts 376). These were largely found to be unsuccessful in the face of competition from radio and television.
The main government TV networks are VRT in Dutch and RTBF in French. The Belgian Dutch are also served by VTM, a private station that developed after the implementation of a 1987 decree that allowed for one private station to be created (Witte 291). The Francophone region is also served by RTL.
Ninety-four percent of Belgian households with televisions are equipped with cable, making it the most densely cabled country in the world. When cable programming first became available, it primarily distributed national programming. In fact, only foreign public service stations were allowed cable access in the Belgian market initially (de Bens 3). Today viewers can access over 30 national and foreign channels. International news programming includes CNN, BBXI, and CNBC.
The Belgian market includes pay channels like Canal Plus and satellite dishes. While there is strong support for expanded television options in Belgian policy, pay television has not become as popular in Belgium as in the United States. For example, after 10 years of operation in Flanders, one such pay venture, Filmnet, only had about 120,000 subscribers. It merged with Canal Plus, but still has not attracted a significant number of subscribers (de Bens 4). Some locations in Belgium also have statutes that limit or prohibit such access.
As of 1997 data, there were over 4.72 million televisions for Belgium's 10 million people ( CIA Factbook ). Like car radios, color televisions in Belgium must be licensed. There are additional fees for cable access (Elliott 185).
While public corporations still own and operate most radio and television systems, private ownership is growing. The public corporations that support public broadcasting receive most of their financial support from the annual licensing fees paid by owners of automobile radios and color television sets. As the economic market continues to influence the media, it is likely that commercial and alternative programming will grow to meet the needs of very specific audiences, while public sponsored media will diminish. In addition, the journalists themselves are occupying more presence in political and social debates.
Electronic News Media
Because Belgium is the most cabled country in the world, the Internet is easily accessible. All agencies, organizations, and government documents are accessible via the World Wide Web. Belgium has several Internet access providers. Belgacom is Belgium's telephone and Internet service provider. Belgium's country code is BE. Skynet is the nation's largest provider because it has a special relationship with Belgacom. Other providers include Aleph-1, Be On, and BIP. The list of providers and free providers is growing in the country daily.
Most large circulation national and regional print newspapers are available online. A survey of web news information sources reveals that the sites are very attractive with lots of color, photography, and links to additional information and news archives. Some publications, such as E-Sports (French), MSR (Dutch), Politics Info (French and Dutch), and Vlaamse Volksbeweging (German, French, Dutch, and Spanish) exist solely online as national publications. Belgian expatriates have several choices for news from home via the Internet, including Expatica.com and xPats.com . The Belgium Post, a foreign publication offered by WorldNews.com , offers daily coverage of Belgium for an English speaking audience. The trend for electronic news is growing because information can be updated throughout the day, and corrections can be made more efficiently.
The European Union is actively involved in creating policies for the dissemination of information on the Internet, including an Internet Rights Observatory. In 1997 Belgian journalists won a case over reuse of their work against Central Station, who had argued that it could reprint their work without permission or compensation.
Education & TRAINING
There are a number of European news organizations and training institutions available to Belgian journalists and editors; while these associations serve greater Europe and/or the European Union, some are based in Belgium itself.
The European Newspapers' Publishers Association (ENPA), a nonprofit organization, represents some 3,000 daily, weekly, and Sunday titles from 17 European countries. More than 91 million copies are sold each day and read by over 240 million people. Based in Brussels, ENPA works toward ensuring a sympathetic European legislative and economic environment for the independent newspaper industry. Its primary goal is to fortify freedom of both the editorial and commercial press. It lobbies for the inclusion of freedom of the press in a Charter of Fundamental Rights to protect newspaper publishers in the event of cross border disputes. ENPA promotes multimedia access and diversity as foundational structures of a democratic nation. Among its other important causes, ENPA actively promotes discussion of intellectual property rights in a technology transformed world; it fiercely defends author ownership of press content against unauthorized reproduction. Finally ENPA would like the European print press to be covered by a more coherent policy like that being drafted and enacted for the Internet.
The European Journalism Centre (EJC), founded in 1992, is an independent, nonprofit multimedia training support center based in the Netherlands, whose membership and services are widely utilized by Belgian journalists, editors, and educational institutions. EJC offers guidance on how to increase European media presence and thereby gain greater and more accurate coverage of European current issues. It provides an assessment of media developments in several countries, including Belgium, and describes the changing nature of Europe's media overall. It also provides media links and tools to help journalists conduct more effective research and to share their working knowledge.
The European Journalism Training Association and its member schools organize and facilitate conferences and colloquia on academic and pragmatic journalism education. It acts as a resource and information broker for its members and provides essays on educational and social challenges facing European journalism programs. The Institut des Hautes Etudes des Communications Sociales and Katholieke Hogeschool Mechelen/Afdeling Journalistiek-De Ham are Belgium member schools.
The International Federation of Journalists (IFJ), based in Brussels, represents over 450,00 journalists in over 100 countries, including the organization's home country, Belgium. The largest of journalist organizations, the IFJ was initially established in 1926 and was launched again in both 1946 and 1952. IFJ exists to promote and defend freedom of the press, social justice, and independent trade union activities. IFJ is nonpartisan, but instead promotes a global human rights agenda. It opposes the use of media for propaganda and/or to promote hate. The IFJ is called upon to represent journalists within both the United Nations and the international trade union movement. It maintains a safety fund for humanitarian assistance for journalistic endeavors. The IFJ agenda is set by a Congress that meets every three years; its actions are carried out by the Brussels-based secretariat who works under the direction of an elected Executive Committee. In addition, since 1992 the IFJ has awarded the Lorenzo Natali Prize for Journalism, one of the world's most valuable journalistic prizes, awarded to print and/or online journalists who have demonstrated a striking insight and particular dedication to the reporting of human rights issues within the context of the development process.
The Pascal Decroos Fund promotes special journalism in the written and audiovisual press in Flanders by granting working grants to journalists who are willing to work on a special project. New and experienced journalists are encouraged to apply. Pascal Decroos (April 20, 1964 -December 2, 1997) was a prominent producer and journalist who died early in his career. He was known as a passionate journalist who promoted the cause of society's underprivileged and who brought a keen and critical eye to investigative journalism. His creed, "do not let yourself be carried along the stream of superficial news, but submerge. Do not content yourself with drawing the obvious conclusion, but investigate and probe until you find the truth," motivated the development of this scholarship that allows journalists to probe a topic deeper and provide more in-depth coverage than the average news story. This working grant is supported by the Flemish community, but is available to any qualifying journalist.
There are also three important media organizations in Belgium. The Association of Belgian Journalists (AVBB) in Brussels, the Belgian Association of Publishers (BVDU), and Febelma, the association of publishers of magazines.
Belgian and European educational institutions offer undergraduate and graduate courses of study in communication and journalism—institutions like Universiteit Leiden, which offers baccalaureate degrees in journalism and news media, Universitaire Faculteiten Sint-Ignatusia (UFSIA), which offers graduate degrees, and VLEKHO and Erasmushogeshool, which both offer postacademic training for journalists. Opportunities to study journalism are enhanced by generous course offerings in the use of technology for investigative journalism and online journalism in both the college and journalism organization settings.
Summary
On the one hand, Belgian press access is expanding with the daily increase of media outlets on the Internet. On the other hand, the coverage offered in mainstream newsprint is becoming more streamlined with media mergers in both the Dutch and the Francophone press. Barriers between French, Dutch, and German speakers continue to grow in this multilingual nation, as is evidenced by a separate higher education system, regional and national news coverage, and economic growth trends in their respective sectors. Press coverage within each region, however, appears to discourage interregional diversity. Smaller political and social movements find the Internet a friendly option for their ideas and publications, as they increasingly find the print media closed to them. While Belgium has sustained internal conflict throughout its history of occupation by different language speakers who ultimately shaped its regional triad, it remains to be seen if Belgium can continue to placate the various groups, as economic success moves closer to the Dutch population, who were once viewed as the inhabitants of a largely agrarian and recession-prone region. The French and German peoples are more and more overshadowed by Flemish radio, publications, and nationalism, which may lead to further conflict.
Belgium's situation as the economic and leadership center of the EU also influences the development of its press coverage. While its role as an economic leader and exporter grows, we must wait to see if its rich culture will be more visible and known to greater Europe and the rest of the world. Information about Belgium's history and culture is still not well documented in the West and English language publications. To further complicate matters, it appears that its EU membership will increasingly determine its position on such matters as freedom of information and Internet commerce.
While Belgium is not hostile to its journalists—it does not license, torture, or imprison them for their investigative work—documented cases of censorship and fines are cause for closer attention. It remains to be determined whether or not technological expansion will ultimately sustain or erode press freedom. While more voices are enabled to provide media coverage—some that have been virtually eliminated or never viable in print—the commercial and compact characteristics of most media present journalists and readers in Belgium with a contradiction. It may be that this contradiction will be sustained and absorbed, as has been the case in most of Belgium's political and social history. It may also be that the news media is changing globally to reduce the gap between entertainment, advertising, and investigative reporting. If that is the case, the news media will further become a menu of options for cultural and selective consumption, thus further reducing the importance of the news media, even as it expands.
Significant Dates
- May 1997: Vers l'Avenir obtains 51 percent of IPM to create near-duopoly situation in the Fracophone press.
- 1998: Le Matin is taken over by Vers l'Avenir, a Catholic publication, thus placing the nation's only remaining leftist paper—whose sales have not improved—at risk of ceasing publication.
- Law enacted that limits press prosecution press releases to the highest public prosecutor. Minister of Justice Tony Van Parys later orders (1999) that prosecutors must designate spokespeople to provide journalist with investigative updates after complaints that the highest public prosecutor was too unavailable for comment.
- 2000: Belga Press Agency enters a joint venture with news aktuell International, a subsidiary of the German Press Agency, to distribute specialized press releases.
- August 2000: A Belgian court grants an emergency injunction to stop L'Investugatuer editor Jean Nicolas from publishing a list of convicted or suspected pedophiles.
- June 2002: Two De Morgen journalists are fined for failing to reveal their sources for a May 11, 2002, story in which they reported that the Belgian State Railway had overshot its budget for a high-speed train. The case will likely join a similar 1995 case on the docket of the European Court of Human Rights, a Strasbourg court that has often affirmed the right of journalists to keep their sources confidential.
Bibliography
de Bens, Els. "The Belgian Media Landscape." In European Media Landscape. European Journalism Centre, 2000. Available from http://www.ejc.nl .
Boudart, Marina, Michel Boudart, and Rene Bryssinck, eds. Modern Belgium. Palo Alto, CA: Society for the Promotion of Science and Scholarship, 1990.
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). The World Factbook. CIA Publications, 2000. Available from http://www.cia.gov .
Elliot, Mark. Culture Shock: A Guide to Customs and Etiquette. Portland, OR: Graphic Arts Center Publishing Co., 2001.
Freemedia. "World Press Freedom Review: Belgium." Freemedia Home Page, 2000. Available from http://www.freemedia.at .
Lamberts, E. "Belgium Since 1830." In History of the Low Countries, Ed. J. C. H. Bloom and E. Lamberts. Trans., James C. Kennedy, 313-386. New York: Berghahan Books, 1999.
Stallaerts, Robert. Historical Dictionary of Belgium. Series: European Historical Dictionaries, No. 35. Lanham, MD: The Scarecrow Press, Inc., 1999.
Witte, Els, Jan Craeybeckx, and Alain Meynen. Political History of Belgium from 1830 Onwards. Trans. Raf Casert. Brussels: VUB University Press, 2000.
World Association of Newspapers. "World Press Trends: On Circulation." World Association of Newspapers Organization Web site, 2001. Available from http://www.wan-press.org .
Sherry L. Wynn
I am doing a business plan for a project where we need to contract a agency with a contact list journalist ( Belgium and EUrope)
May I have the prices for your services,
Many thanks
VIrginia Aguilera